Observing the issued standards for factory design will help investors and businesses ensure the overall quality of the construction project. Let’s explore the latest factory design standards with Pebsteel in the following article.
1. 6 latest industrial factory design standards
Today, legal bases have issued standards for constructing factories to ensure that the construction and operation processes of the factory adhere to the latest regulations. These documents clearly define the categories of design standards that investors, design contractors, and construction contractors must strictly adhere to. These include the Vietnamese Construction Standards according to Decision No. 682/BXD-CSXD dated December 14, 1996, and the Vietnamese Construction Standards according to Decision No. 439/QD-BXD dated September 25, 1997, by the Ministry of Construction.
See more: Quotation Of Warehouse Construction Costs Updated In 2025
1.1. Factory floor design standards
Regarding the standards for designing the factory floor, customers need to comply with the requirements for the structural drawing of the factory floor as specified in TCVN 2737:1995. It is to ensure that the technology for load-bearing capacity, geological conditions of the construction site, and hydrogeological conditions will meet the following factors:
- For designing the floor of a manufacturing workshop on weak soil, it is necessary to apply appropriate ground treatment measures following the geological conditions.
- The design of the floor for a production workshop must adhere to the requirements of technology and usage conditions to select a suitable floor structure for different types of floors, such as concrete floor, steel floor, tiled cement floor, or wooden and plastic composite floor.
- It must ensure a level surface if designing the floor for the warehouse and yard area in a dry area used for unloading bulk materials.
- The factory floor should have a sturdy underlayment and an effective drainage system to prevent water accumulation.
- The factory’s concrete floor must be divided into squares, with each square having a maximum length of 0.6 meters. Additionally, bitumen must be inserted between the grid squares. The concrete underlayment must have a minimum thickness of 0.1 meters, and the sidewalk should have a width ranging from 0.2 to 0.8 meters with a slope of approximately 1 to 3%.
See more: Prefabricated Factory Structure
1.2. Foundation design standards
- The standards for designing the foundation drawings of the factory and the technical systems of the underground construction section should be designed following the geotechnical properties of the soil foundation and the natural characteristics of the construction site. In particular, the foundation standards must adhere to the necessary regulations when designing foundation drawings.
- The designs for the foundations of the workshop buildings all have the height of the top surface of the foundation lower than the ground level, with specific differences as follows: Steel columns: a difference of 0.2 meters; columns with embedded wall frames: a difference of 0.5 meters; reinforced concrete columns: difference of 0.15 meters.
- For the height of the base of steel columns in the corridor, elevated walkway, and pipe supports between workshops, it is mandatory to be higher than the minimum floor level by at least 0.2 meters.
- In designing column foundations for the factory, incorporating expansion joints, and anticipating the expansion of the workshops, the owner must ensure a unified procedure for two adjacent columns.
- If these are foundations under brick walls, constructed walls, or stone blocks in cases where the building does not have a column frame, the depth of the foundation should be equal to or less than 15 cm. Designing wall support beams in this scenario is necessary, and the top surface of the support beams should be at least 3 cm (0.03m) lower than the finished floor level.
- The foundation of the factory must be built with a heat-resistant material protective layer in order to withstand exposure to high temperatures. The best solution for foundations subject to corrosion is to use corrosion-resistant materials.
See more: Mechanical Factory Design Standards and Procedures
1.3. Factory roof and dormer design standards
Similar to other parts of the construction, the roof also has specific design standards. Specifically, the slope of the roof will depend on the material used for roofing:
- Roofs made of asbestos cement typically have a slope ranging from 30% to 40%.
- Corrugated metal roofs will have a slope of about 15% to 20%.
- Tiled roofs will have a slope ranging from 50% to 60%.
- The slope is usually only 5% to 8% for roofs covered with reinforced concrete panels.
Regarding the design of rainwater drainage, specific standards for each type of roofing material must be met:
- For structures with multi-pitched roofs, the drainage system can be designed either inside or outside, depending on the overall drainage system of the construction.
- In the case of a single-pitched roof in a workshop, rainwater will flow freely without the need for a separate drainage system for the roof. However, if the height of the house column is 5.5 meters or higher, the customer will need to design a gutter system to channel the water down.
Read more: Standard Factory Construction Process
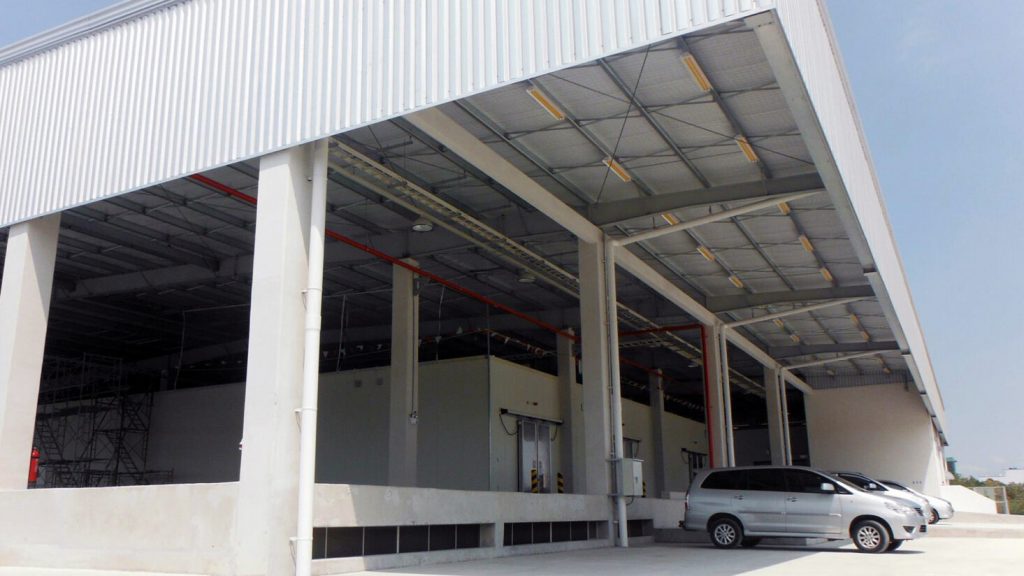

1.4. Factory wall and partition design standards
Similar to other parts, depending on the specific industrial project, a type of wall will be suitable for the future operational process. There are three common types of walls in industrial workshops: load-bearing walls, self-supporting walls, and frame-inserted walls.
The following important point in the project’s wall section is designing the wall’s base. Specifically, the owner must design the waterproofing part using bitumen or other materials. This moisture-resistant layer is created using cement mortar with a thickness of about 20cm. For partition walls, the investor can use materials such as reinforced concrete plastic, veneered wood panels, mesh reinforced with wooden or steel frames, etc.
1.5. Factory window and door design standards
There are 3 standards for designing windows and doors for industrial workshops:
- The essential requirement when designing a door is that it must open outward. Additionally, the dimensions of the entrance door should be compatible with the types of transportation used in the company’s operations.
- Customers should note that the height of the door should be at least 2.4 meters from the floor.
- The windows of the factory need to be designed with a mechanical system for opening and closing.
1.6. Some other industrial factory design standards
In addition to the mentioned standards, investors should also pay attention to other requirements of industrial workshops, including:
- Adhering to the standards related to the electrical system of the construction to ensure safety and efficient use.
- Firefighting systems are an indispensable element in industrial workshops. When designing, it is necessary to comply with Government Decree No. 79/2014/ND-CP.
- Observing design standards related to security cameras, lightning protection, or waste treatment systems.
2. Industrial factory design standards for some export industries
Compliance with the current regulations of the six standards is required, and each export industry has its own specific requirements. Let’s take a look at some design standards for factories in specific export industries with Pebsteel:
For the interior furniture export industry, the workshop needs to meet the following standards:
- Flexible space: The factory should have flexible space to accommodate the production of various sizes and shapes of interior furniture products.
- Wood processing area: Designing a standardized wood processing area is crucial, including areas for cutting, sanding, and finishing wood.
- Occupational safety: Industrial areas should be designed with safety measures to protect workers and prevent potential hazards.
For the seafood export industry, the workshop needs to meet the following standards:
- Specialized seafood processing area: Customers must ensure that the factory has specialized zones for seafood processing, guaranteeing cleanliness and food safety.
- Storage area: The storage area should be designed to efficiently and safely store and transport seafood products.
You should pick a reputable and knowledgeable company to ensure the construction meets these exacting standards. Pebsteel offers comprehensive pre-engineered steel building solutions in over 50 countries, covering 6,000+ projects of various scales, from minor to mega-structures, with a team of over 1,400 engineers with years of experience. Additionally, Pebsteel has a wealth of experience designing industrial factories for various industries, including export-oriented ones like producing leather goods and automobiles.

Conclusion
Above are the details about the latest 6 standards for industrial factory design and some additional standards for export industries. If you seek comprehensive solutions for Pre-Engineered Buildings, Steel Structures or structural steel design, please contact Pebsteel via email at Marketing@pebsteel.com.vn or by phone at +84 908 883531 for immediate consultation.
*** This article is intended to provide general information about the pre-engineered steel building and steel structure industry only. For further details or clarification based on your needs, please contact Pebsteel directly.