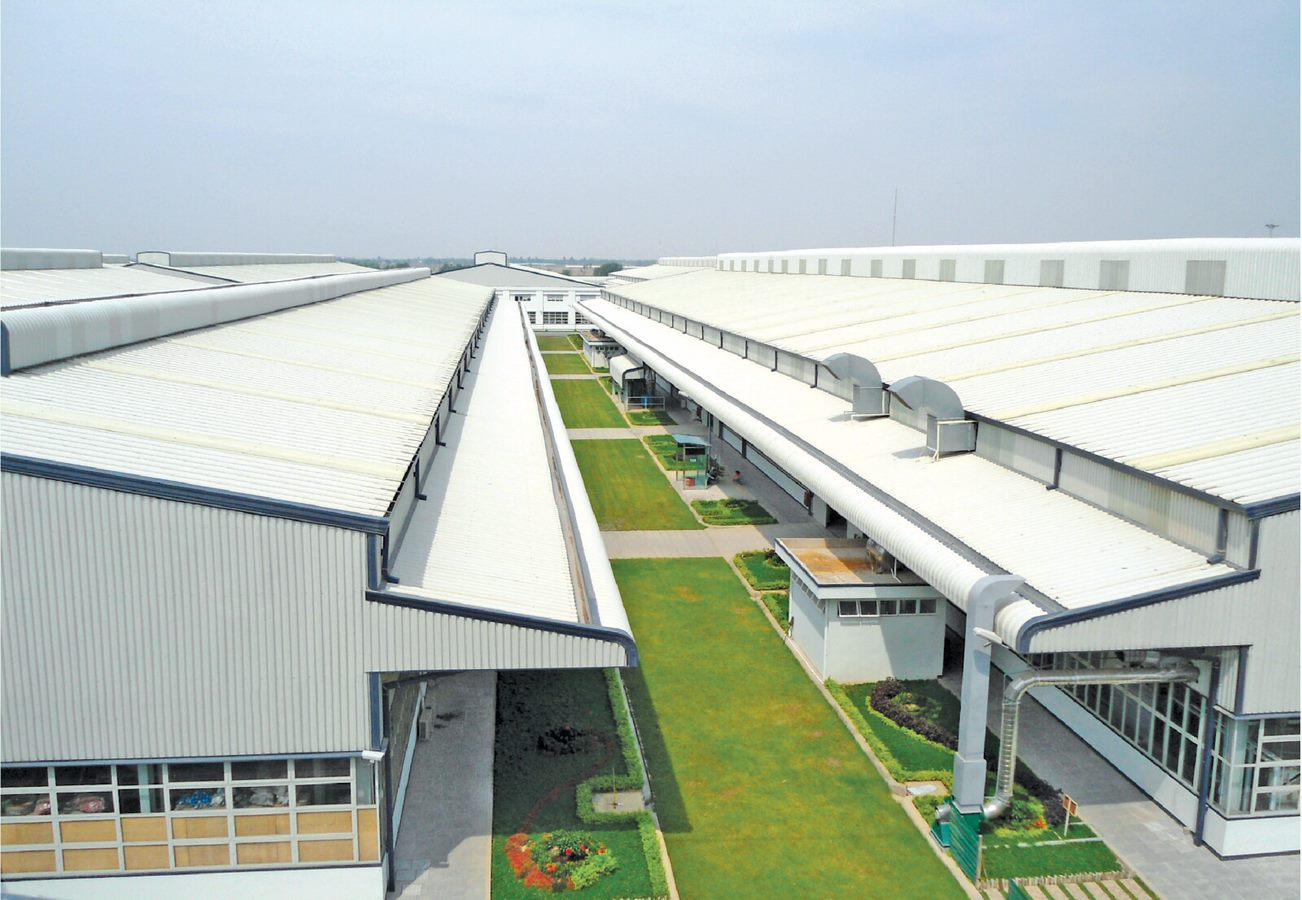
In the fast-paced world of modern industrial architecture, the need for cost-effective and rapid construction solutions is greater than ever. Pre-engineered buildings are transforming how developers and businesses plan and build spaces. These structures utilise pre-designed and manufactured steel components that are assembled on-site, offering fast construction, cost savings, and design flexibility. As a trusted industry leader in steel structure fabrication in Vietnam, Pebsteel understands that projects today require more than speed; they also require structural integrity. This pre-engineered building guide lays the groundwork for understanding what a pre-engineered building is, how it works, and why it has become a smart choice for modern construction.
1. What are Pre-engineered Steel Buildings?
Pre-engineered steel buildings are modern facilities that use steel frames. These frames are precisely fabricated in a factory and then quickly assembled on-site. This method ensures durability, rapid construction schedules, and flexible expansion capabilities. Because of their standardised components, these steel storage buildings can be extensively customised to suit specific storage needs, optimise goods circulation flows, and withstand various regional climatic conditions.
The pre-engineered building (PEB/PEMB) system is a comprehensive one. It includes the primary framing (columns and rafters), the Z and C purlin systems, metal roofing and wall cladding, and a complete suite of synchronised accessories. Every component is cut, welded, and painted within the controlled manufacturing facility. It is then transported to the site for assembly using bolted connections. This disciplined process ensures rigorous quality control and substantially mitigates the construction risks often associated with adverse weather conditions.
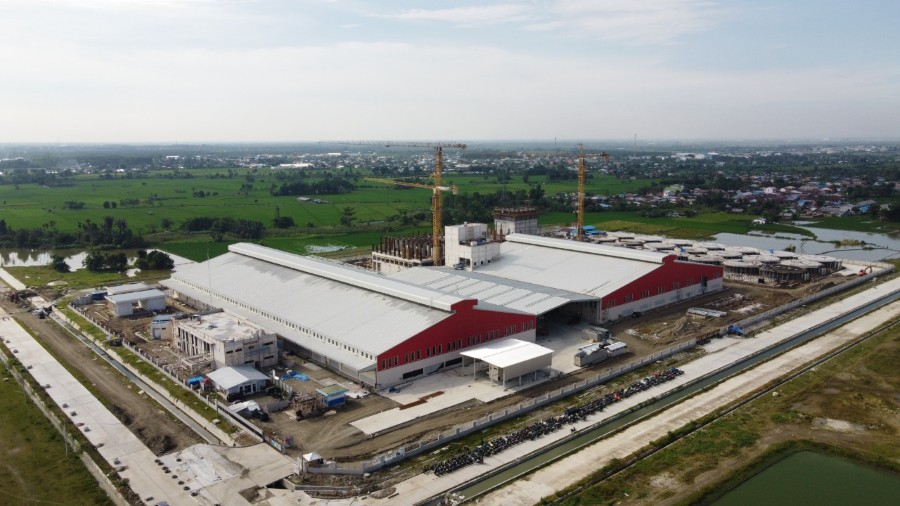

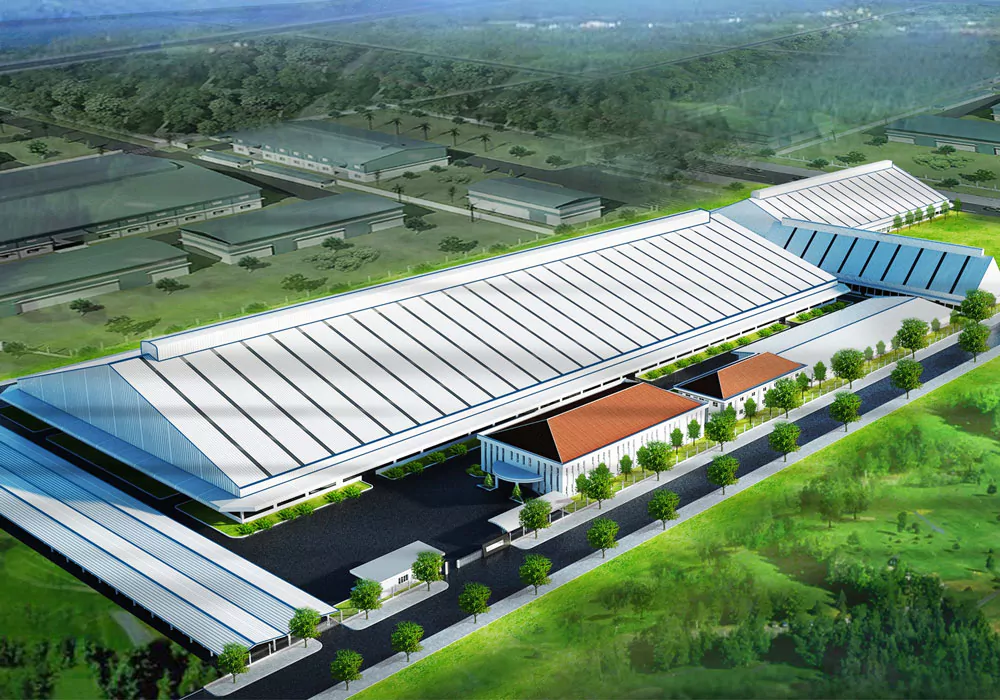
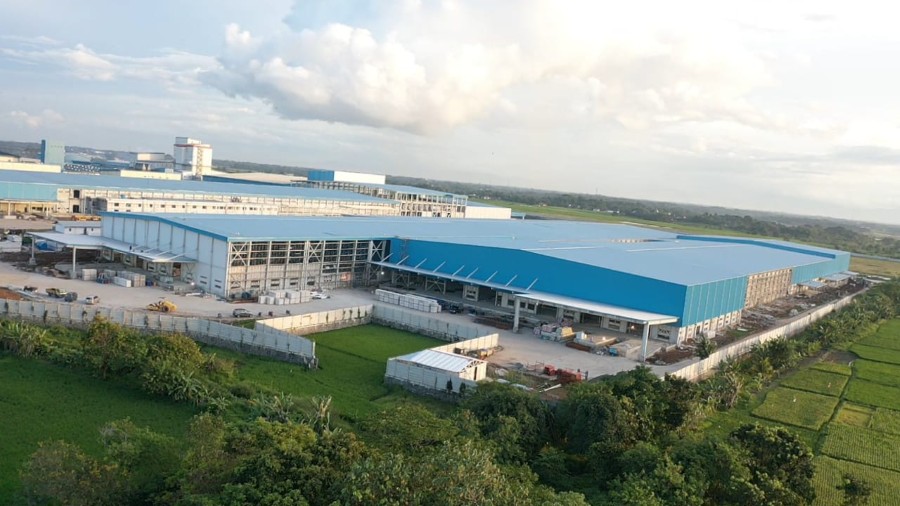
A pre-engineered steel factory designed by Pebsteel is in operation
2. Key Characteristics and Operational Efficiency of Pre-Engineered Buildings
The defining characteristic of a modern pre-engineered building is its spatial efficiency. The clear-span design effectively eliminates the need for intermediate columns, thus creating an unobstructed interior. This open space is crucial for optimising forklift maneuverability and streamlining critical loading and unloading operations. Such architectural freedom is particularly advantageous for any metal storage building housing bulky machinery or voluminous inventory, especially when integrated with wide-opening industrial door systems.
Design Flexibility and Future Scalability
Flexibility is a major hallmark of the pre-engineered system. Future scalability is inherent to the design; expanding the facility involves extending the frame length or increasing the eave height, a highly streamlined process. This adaptability perfectly accommodates business growth without causing major operational disruptions.
Building Envelope and Environmental Control
The building envelope offers versatile configuration options. For basic storage needs, single-skin metal sheeting may be sufficient. However, for facilities requiring strict environmental control, insulated composite panels with PU or Rockwool cores, provide superior thermal and acoustic insulation. Rockwool can also improve the fire resistance rating of warehouses and factories, ensuring compliance with strict safety regulations while safeguarding valuable assets.
Furthermore, integrating passive ventilation systems and natural lighting (such as skylights) significantly reduces the facility’s reliance on artificial energy sources. Ultimately, the specific configuration of the structure, whether for a steel storage building or a complex factory, depends on local climatic conditions, the required level of asset protection, and the balance between the initial investment and projected long-term operational costs.
Pre-engineered buildings (PEB) are defined by their structural efficiency, design adaptability, and use of highly recyclable steel materials. This powerful combination of adaptability and sustainability makes them the preferred choice for forward-thinking enterprises globally.

Essential Attributes and Operational Performance
Read More: Trusted Steel Structure Design Solutions for Industrial & Commercial Use
3. Pros and Cons of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
A steel storage building delivers undeniable value through durability, low maintenance requirements, rapid erection, and customisation flexibility. However, to ensure the structure’s longevity, investors must pay close attention to thermal insulation, condensation control, leak-proof detailing, and corrosion protection suited to the specific environment.
To provide you with an accurate perspective, Pebsteel has outlined the specific advantages and considerations when constructing a pre-engineered building.
3.1. The Advantages
The primary appeal of this construction method lies in its efficiency. PEBs reduce material and labour costs and shorten construction timelines. Standardised manufacturing and assembly processes also help minimise risks during construction.
- Durability & Resilience: Steel materials are immune to termites, highly weather-resistant, and boast a long service life. The ability to customise dimensions, colours, and accessories makes these structures suitable for a vast array of industries.
- Operational Optimisation: The clear-span design, combined with wide openings and significant clear height, creates an ideal environment for forklifts and trucks to maneuver. Selecting the correct dimensions and opening sizes ensures that large equipment can enter and exit with ease.
Economic Scale: As the project area increases, the average cost per square meter tends to decrease due to economies of scale, making it a financially sound choice for large metal storage building projects.

Advantages and Limitations of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
3.2. The Considerations (Cons)
While robust, the metal envelope requires specific technical attention to maintain performance:
- Environmental Control: Without proper insulation or anti-condensation films, metal cladding can lead to condensation buildup and significant rain noise. It is essential to strictly follow design and installation guidelines for the building envelope, ensuring tight detailing at the ridge, eaves, and roof penetrations to prevent leaks.
- Corrosion Management: Projects located in coastal areas or highly corrosive environments require specialised protective coatings and a strict maintenance schedule.
- Compliance: Investors must strictly adhere to local building regulations and permitting requirements before commencing installation.
PEBs offer several advantages, including fast construction, durability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. They are a smart solution that aligns with modern construction trends. By understanding both the strengths and the technical requirements, businesses can maximise the value of their investment.
4. Types of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
Classifying pre-engineered building systems by structural geometry, functionality, or enclosure solutions allows investors to select the optimal configuration for their land area, goods flow, and budget.
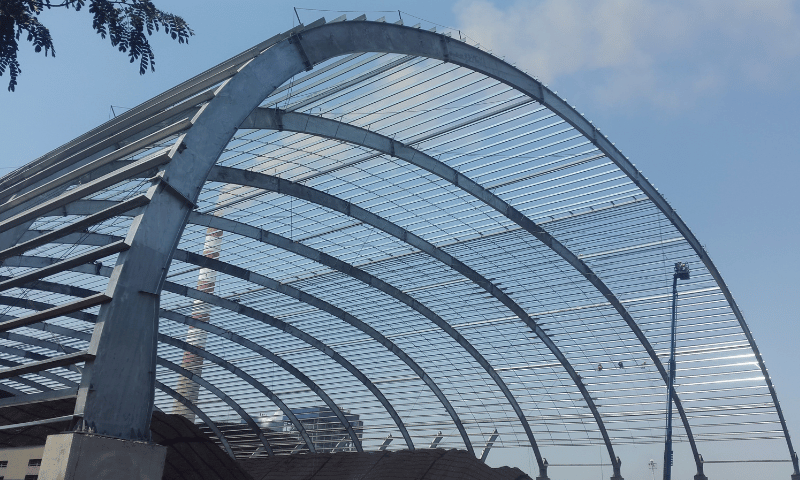

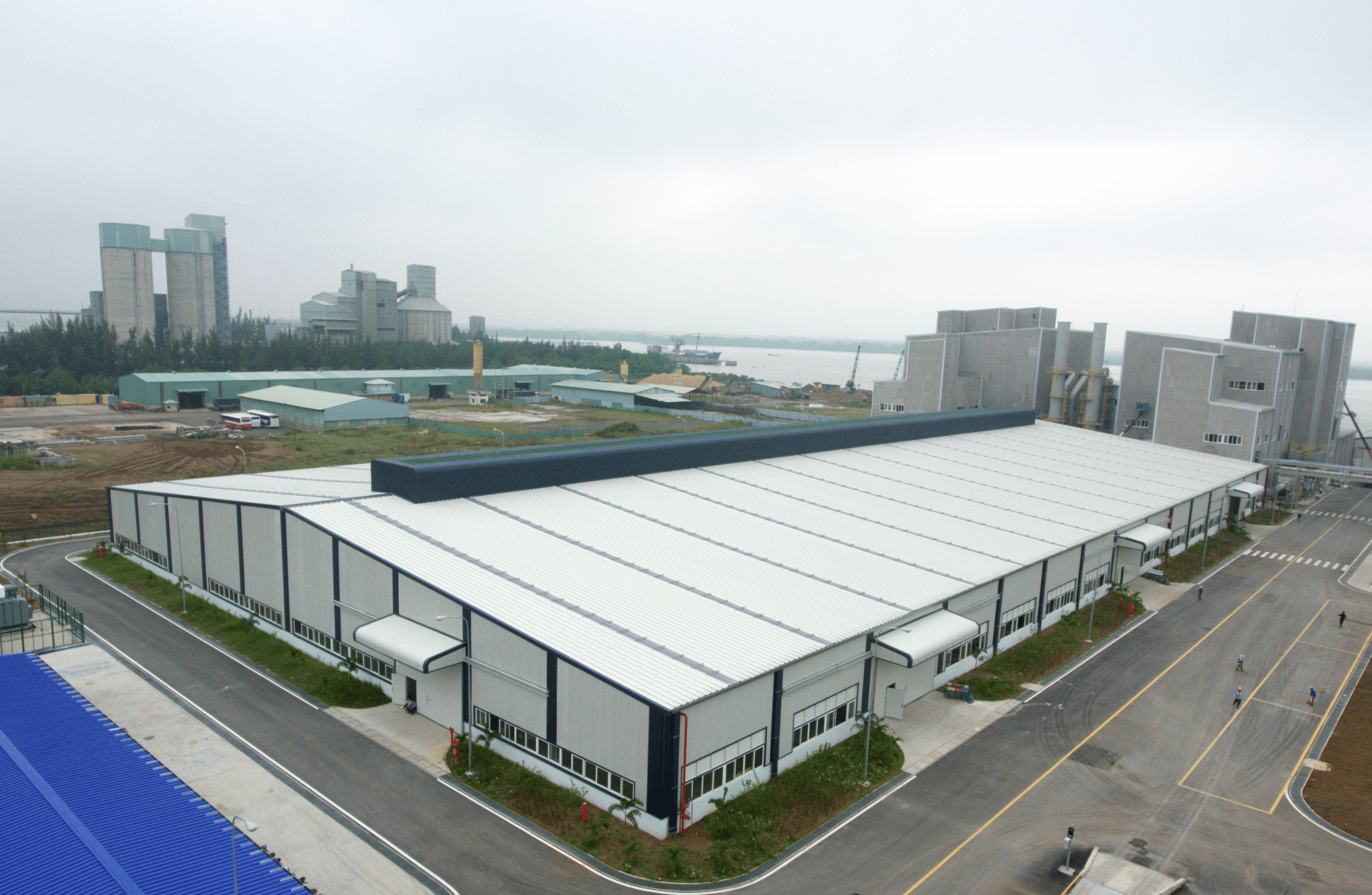
Pre-engineered building constructed by Pebsteel
4.1. Classification by Structural Geometry
The shape of the steel frame dictates both the aesthetic and the functional capabilities of the metal storage building.
- Gable Frames (Double Slope): Ideal for large spans and easily expandable. This is the most common profile for general storage.
- Single-Slope Frames: These feature one-way drainage, making them useful for narrow plots or when orienting the roof for solar panel installation.
- Multi-Span Frames: These utilise interior columns to reduce steel weight across very wide buildings, offering a cost-effective solution for massive logistics centres.
- Arch/Quonset Style: A self-supporting structure that is fast to install with fewer complex details.
Regardless of the configuration, Pebsteel emphasises the importance of checking roof slope, purlin spacing, bracing, and leak-proof detailing at the ridges and eaves to maintain the integrity of the building envelope.
4.2. Classification by Function
The versatility of steel structures is vast. PEBs are used in various types of projects, including industrial (factories, warehouses), commercial (showrooms, offices), infrastructure (stadiums, stations), and residential (houses, urban areas) developments. Each application is optimised according to structural type and technical requirements.
- Logistics Warehouses: These prioritise high-frequency input/output. Design focuses on loading docks, dock levellers/shelters, and truck buffer zones to enhance handling efficiency.
- Cold Storage: Requires thick insulated panels, specialised cold-storage doors, and strict humidity/condensation control.
- Self-Storage: Prioritises modularity and security partitioning.
Unlike manufacturing plants (which require forced ventilation and foundations capable of withstanding heavy machine vibration), a steel storage building focuses on storage capacity and flow. Therefore, the structural design, MEP, and foundations are often “lighter,” prioritising clear-span area and large openings.
4.3. Enclosure Systems and Openings
The enclosure system plays a critical role in protecting a pre-engineered building from weather, enhancing insulation, and ensuring long-term durability. Key components include:
- Cladding Materials: Single-skin metal sheets suit basic needs, while PU or Rockwool sandwich panels are essential for thermal and acoustic efficiency, as well as reducing condensation.
- Waterproofing: The system of seals (gaskets, sealants), trims, flashing, ridge caps, and gutters acts as the critical “link” to prevent leaks.
- Door Systems: When selecting rolling doors, sliding doors, or overhead doors, consider the clearance height and wind/sun orientation.
4.4. Operating Accessories
To maximise efficiency, modern warehouses integrate smart accessories:
- Energy Efficiency: Skylights, louvres, and turbine vents reduce reliance on artificial lighting and power for ventilation.
- Loading Bay Efficiency: Dock levellers and shelters shorten the cycle time for trucks entering and exiting, which is particularly effective for cold chains.
- Drainage: A robust system of gutters and downspouts ensures rapid rainwater drainage, preventing roof overload and edge seepage. This system requires seasonal maintenance to ensure longevity.
5. The Construction and Erection Process of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
Generally, the lifecycle of a pre-engineered building project encompasses six critical stages: survey and design brief, technical design, factory fabrication, on-site erection, enclosure finishing, and finally, handover. Throughout this cycle, strict adherence to foundation requirements, site preparation, and local permitting is mandatory.
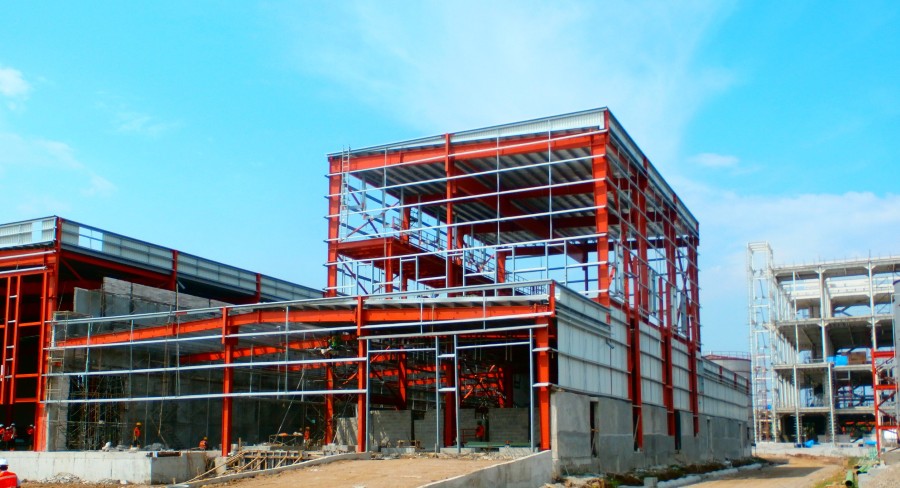

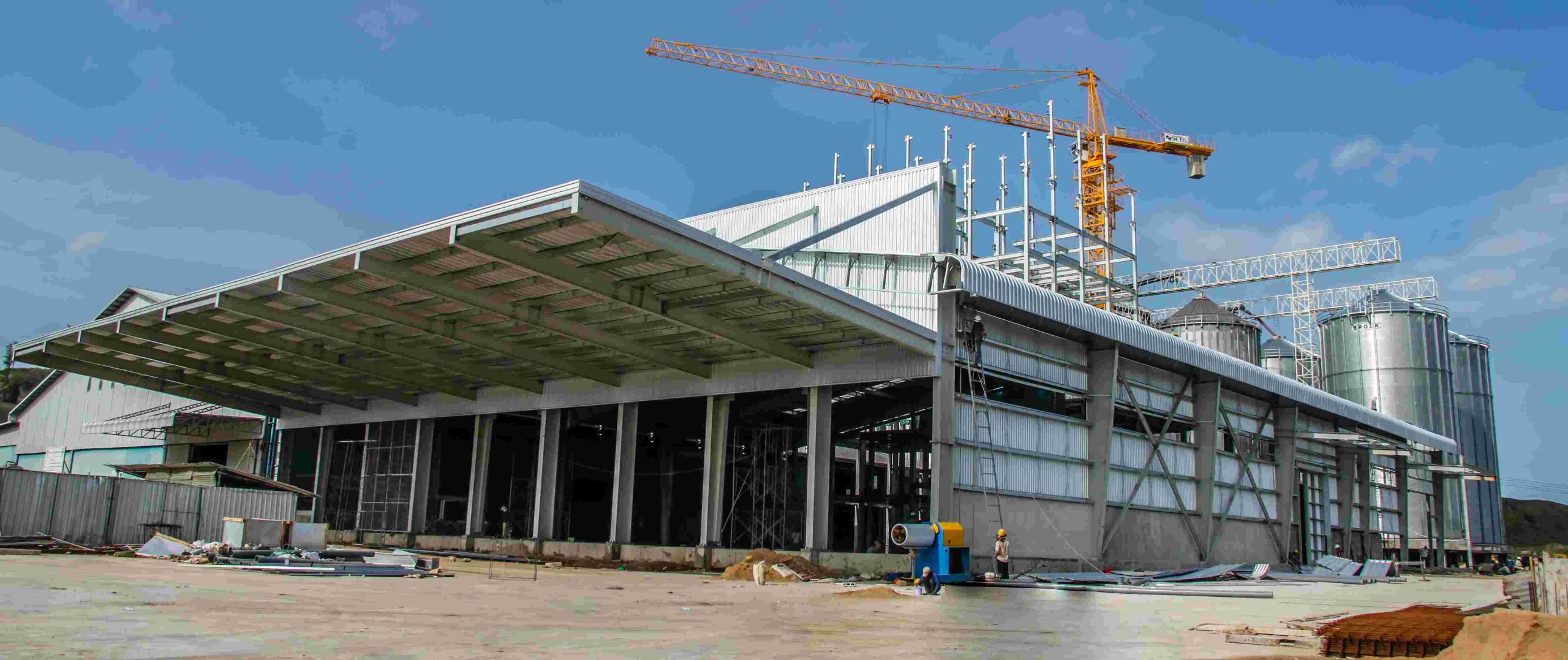
Construction and Erection Process of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
5.1. Site Survey and Design Brief
This foundational step involves geotechnical surveys and analysing wind loads, floor elevation, and truck turning radii. It identifies key dimensions (span, column spacing, height) and goods flow. These inputs determine the optimal frame configuration, opening sizes, and insulation levels for the steel storage building. The design brief must clarify applicable standards, functions, milestones, and local building codes (bylaws) to prevent costly legal or structural issues later.
5.2. Technical Design and Detailing
Engineers calculate the primary frame, bracing systems, and purlins, checking for stability and deflection while designing moment connections and bolting details. Detailed “shop drawings” are generated to specify component codes, hole positions, and assembly sequences, drastically minimising on-site errors. Simultaneously, the roof and wall systems, insulation, condensation control, and lighting/ventilation solutions are finalised based on climate and function. Opening dimensions must be validated to accommodate the largest equipment or vehicles expected to enter.
5.3. Fabrication and Quality Control
Components are cut, welded, surface-cleaned, and painted according to strict standards. Quality Control (QC) verifies dimensions, paint thickness, and material traceability to ensure quality standards are met. Each item is marked by zone to accelerate on-site handling. Prior to erection, preparing the foundation, drainage, and temporary access roads for cranes and trucks is a prerequisite to ensuring long-term structural stability.
5.4. On-Site Erection
This is a critical construction phase where the erection team installs columns and rafters precisely along the established grid lines. Bolts are meticulously aligned and tightened to the specified torque. Following the main frame, purlins, bracing, and the building envelope are installed sequentially to ensure complete spatial stability. Strict safety measures are mandatory throughout this process, including the use of scaffolding, harnesses, and continuous monitoring of wind speed. Once the main frame is fully stable, the team proceeds to install weather-sealing details at the ridges, eaves, and all penetrations. Stage-by-stage inspections are conducted immediately to rectify any structural deviations or errors.
5.5. Finishing: Enclosure and Accessories
The final enclosure involves the installation of essential accessories. Ridge caps, trims, gutters, downspouts, and flashing are installed in a precise, logical order. All joints are then thoroughly sealed to prevent water leakage and internal condensation. A water-tightness test is highly recommended after the first major rainfall to fine-tune the system and confirm leak resistance. Finally, operational systems are installed and tested. This includes rolling, sliding, or overhead doors, dock levellers, shelters, lighting fixtures, and turbine vents. These components are critical for ensuring both safe evacuation routes and smooth, efficient cargo flow within the completed facility.
5.6. Handover, Operation and Maintenance
The handover package includes acceptance checklists, as-built drawings, operation manuals, and a suggested maintenance schedule. Recording component codes facilitates rapid replacement when necessary. Investors should establish a schedule to inspect the roof, fasteners, gutters, and coatings from day one. Periodic maintenance is the key to sustaining the warehouse’s performance.
During the construction of a metal storage building, the contractor must strictly adhere to fire safety regulations. This ensures a safe environment for workers. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties from local authorities. Furthermore, using materials like Rockwool panels contributes significantly to the fire resistance rating of warehouses and factories, a critical factor for long-term operational safety.
6. Maintenance of Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
Proper maintenance is the lifeline of any pre-engineered building. It prolongs the structure’s lifespan, mitigates leak risks, and keeps operational costs within a reasonable range. We identify 5 “pillars” of effective warehouse upkeep: periodic inspection, coating hygiene, condensation control, and strategic retrofitting.

Maintenance Guidelines for Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings
6.1. Periodic Inspection Schedule
A strict observation schedule is essential for the roof, wall cladding, self-drilling screws, sealing gaskets, and roof penetrations. Following heavy storms, it is imperative to re-check bolts, edge trims, and potential leak points. Gutters and downspouts must be regularly cleaned to prevent water stagnation and overflow at the eaves.
Early detection and treatment of leak points prevent disruptions to the supply chain and stop damage from spreading, which is particularly critical for steel storage buildings housing moisture-sensitive goods.
6.2. Cleaning and Coating Preservation
To prevent corrosion, the building envelope should be cleaned with appropriate solutions to remove accumulated dust, sea salt, and grease. Inspectors should check for peeling paint or scratches to address rust risks immediately.
Performing touch-up painting and localised rust prevention before the rainy season is a proactive practice.
6.3. Condensation Control and Ventilation
Effective solutions include inspecting insulation layers, anti-condensation films, and tape at panel joints. Details at the ridge and end walls require careful review, as these are prone to moisture accumulation.
For enclosed areas, optimising natural ventilation (via louvres or turbine vents) or installing industrial fans is crucial. Adjusting airflow according to the season helps stabilise the microclimate and save energy, especially in hot and humid regions. Note: When upgrading insulation to control temperature, facility managers should also consider materials that enhance the fire resistance rating of warehouses and factories, ensuring safety alongside efficiency.
6.4. Retrofitting and Upgrades for Metal Storage Buildings
A metal storage building is inherently highly adaptable, allowing for future modifications and enhancements. Owners can easily retrofit the facility by replacing aging single-skin metal sheets with modern insulated panels or by installing standard skylights, thereby significantly increasing natural light penetration.
If the operational demand within the facility changes significantly, such as an increase in racking loads or the need for new overhead cranes, the existing structural frame must be recalculated for necessary reinforcement. In critical loading zones, updating existing equipment can yield major efficiency gains. Implementing newer dock levellers, high-speed doors, and advanced safety equipment can significantly shorten vehicle cycle times. Furthermore, upgrading the gutter and downspout system is strongly recommended if the local rainfall intensity increases seasonally, ensuring optimal water drainage and protection for the building envelope.
6.5. Maintenance Logs and Cyclic Repainting
Recording specific items, dates of execution, and materials used allows for easy traceability during warranty claims and future planning. For buildings in highly corrosive coastal environments, adhering to a strict repainting cycle is vital to maintain both aesthetics and durability.
A consistent maintenance cycle ensures that the pre-engineered building operates stably, avoids downtime, and optimises long-term operational costs.
7. Cost Factors for Pre-Engineered Steel Warehouses
The investment required for a pre-engineered building (PEB) is not a fixed number, it inherently fluctuates based on specific technical parameters. Key cost drivers include the building’s dimensions (such as clear span and eave height), the required insulation levels, the quantity of industrial doors and loading docks, the project’s site location, and the complexity of the foundation and drainage systems.
Notably, the principle of economies of scale is particularly significant in this sector: as the project scale increases, the average cost per square meter typically decreases. Therefore, investors are strongly encouraged to consider the “total lifecycle cost”. This approach integrates operation and maintenance expenses alongside the initial capital expenditure, which is crucial for finding the optimal balance between upfront investment and long-term usage efficiency.
A factory or a steel storage building represents a significant corporate asset. Its configuration impacts not only the construction budget but also the enterprise’s future production capacity and overall operational flow. To gain a deeper understanding of the necessary cost categories, it is advisable to explore expert insights on Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings Construction Unit Prices.
With over 30 years of experience in the design, manufacturing, and erection of pre-engineered steel buildings and structural steel, Pebsteel is committed to delivering optimal, efficient, and sustainable solutions for businesses both locally and internationally.
If you are looking for comprehensive solutions in steel structure construction, contact Pebsteel via email at marketing@pebsteel.com.vn or phone: at (+84) 908 883 531 for consultation!
Disclaimer: This article is intended for general information purposes regarding the pre-engineered steel and structural steel industry. For specific details or clarification based on your project needs, please contact Pebsteel directly.